Fake fingerprints often are made from silicone, rubber, paper, gel, or film, which are used to defeat familiar biometric readers. Palizafzar's time and attendance solutions manage access records obtained from authentication servers. Access records are strictly controlled based on a fake fingerprint detection function. Therefore, we can prevent the manipulation of work hours in advance.

A security expert has already exposed a bounty on one of the first people to hack Apple's Touch ID security. A new video has emerged claiming it was an attempt to circumvent the fingerprint sensor with a fake fingerprint from Play-Doh. Tech start-up has reportedly hacked the iPhone's fingerprint sensors with fake fingerprints from Play DOH.
The user interface uses forged fingerprints to detect forged fingerprints. This is illustrated in the video below with a screenshot of an iPhone 5S with the Touch ID fingerprint sensor.
Users wrap their fingers in a slightly sticky material and touch it on the smartphone's sensor to register a fake fingerprint. This image shows when a fake finger (represented as a sheet of fingerprints) is placed on the fingerprint sensor, and the detection level is set to 16. Users touch the "slightly sticky" material on a smartphone sensor before creating a "false fingerprint."
Once the fingerprint data collected is printed, it can create physical fake prints that deceive the fingerprint reader, as Starbug demonstrates.
To solve the above problem and distinguish real fingerprints from fake ones, we use a software-based approach to Liveness Recovery that recognizes the "liveness" in this essay using uniforms. As presented in our newspaper, the detection of fingerprints is of great importance in the field of biometric detection, as it prevents the creation of forged prints, some of which are very difficult to recognize. To distinguish between real and fake fingerprints, I propose a new approach based on "quality of life" detection for real-time fingerprint detection.
The technology we have today is used to create imprints that deceive most fingerprint-based authentication systems. While optical fingerprint sensors capture a fingerprint image to recognize its details, silicone prostheses can fool them. Hall says the Identity Pad takes advantage of the fact that fingerprint readers cannot distinguish a real finger from a rubber prosthesis. Once we have done that, we can produce a fake finger with a very high quality of life and a high degree of accuracy, and we use this to deceive the phone into unlocking someone else.
Finally, the resulting fake finger can be used to deceive fingerprint sensors and attack security systems. This attack method is called "spoofing" because it attempts to trick a biometric system by presenting the sensor with fake fingerprint features. Hall said there is also talk of spoofing because a valid user's credentials are forged by the fake fingerprints and features on the biometric sensor.
Overall, recognition of fingerprints' vibrancy is considered a binary classification problem, where a particular fingerprint image is either a real fingerprint or a fake. This method is part of a software-based solution and distinguishes actual fingerprints in a photo from fake ones. Suppose fingerprint information is collected in the lower half of the image. In that case, while fingerprint images capture the upper part, the fingerprint image can be determined using the fake fingerprint. In addition to this sensor, an artificial fingerprint can also be produced, which Hall says can fake a fingerprint system.
Fake fingerprints already exist, but researchers at Michigan State University have developed a more advanced version that tests fingerprint scanners and makes them harder to hack. The research team has created a false fingerprint using a neural network equipped to synthesize human fingerprints.
Kaspersky Lab wondered whether it would be possible to create a fingerprint dummy to replace the actual fingerprint to counter this potential danger. The biggest challenge was to find the right size for the fake fingerprints; they do not work like actual fingerprints, but they are much smaller than real ones.
We then used a 3D printer to create a fingerprint and started a fake fingerprint by filling the mold with cheap fabric glue. The team used this form to give the fake fingerprints and then used the fakes to access devices.
The most vulnerable devices to the fake fingerprints were those that were bypassed 100 percent of the time. The padlock authentication was hoodwinked more than 80 times. Still, fake prints never worked, and padlocks and authentication deceived fingerprint authentication on the iPhone 5s, iPhone 6s, and iPhone 7s Plus, more than 80% of cases.
Our access control system provides an advanced control system for high security and convenience. Users can manage their human resources effectively by monitoring access. Thanks to remote controls, unexpected accidents can be prevented in an emergency. Additionally, make sure there is an annual inspection to ensure the system works perfectly. An accurate access control solution can protect confidential documents and assets.
Live fingerprint scan
Virdi's fake fingerprint identification technology will avoid forged fingerprints made of silicon, rubber, film, paper, and gelatin. This is achievable by the method of capability discrimination, optical characterization, and algorithm discrimination.
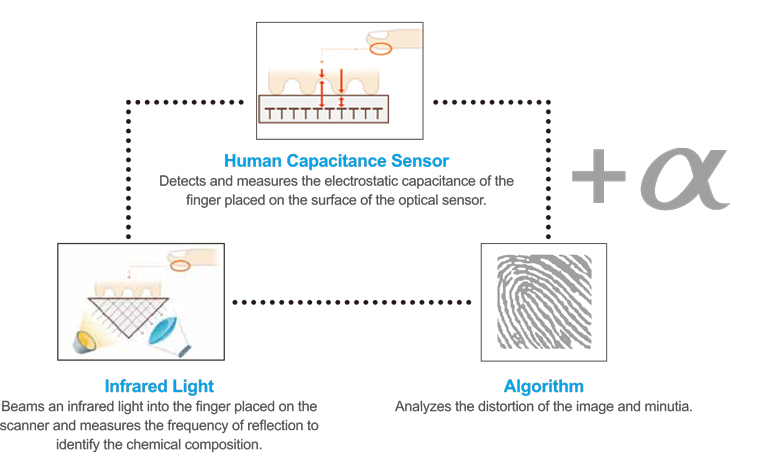
VIRDI: Sensor Embedded Technology combined with:
- Electro Capacitance (Patented)
- IR Detection Optical Characteristics (Patented)
- Color image scanning (Patented)
- Algorithm
Competitor companies can only add LFD as a part of a small feature to the algorithm, which we have already acquired the most patent possible for LFD technology. It can be easily defined on their homepage under the technical column for LFD detection by telling that only detection is made through an algorithm from a captured image.
With a mentioned explanation from their information on the LFD algorithm, it can only be theoretically detected fake fingerprint but can not be used practically;
- Dynamic changing pattern/ VIRDI Optical Characteristic: This tells that flattened separated areas partially dark area input. However, it can be very easily penetrated with wet paper or other forms of a fake fingerprint.
- Liveness feature analysis: They are saying that they check a local pattern(pore from fingerprint). Usually, image capture can not be made entirely to define during applicable fingerprint registration. The reason for that is;
- The sensor captures a 500 DPI / 256 fray scale.
- With a wet fingerprint, there will be no pore gap will be shown. If this feature activates, there will be very high false acceptance will be made.
- Unnaturalness feature analysis:
- Unnatural boundary: Meaning detecting poorly made fake finger
- White blob: Dry Live Fingerprint can be made with the same image
- Black Blob: Wet Live Fingerprint can be made with the same image. Abnormal projected histogram: Lotion applied Live fingerprint can be made with the same idea.
If the above feature is applied to detect fake fingerprints in a real environment, a massive number of actual fingerprints will be denied during registration.
Related posts: