Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has transformed how businesses manage access control and attendance systems. By using electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects, RFID eliminates the need for manual attendance recording or traditional access cards. Its non-invasive, automated nature makes it an ideal choice for enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of modern access control solutions.
How RFID Technology Works: A Technical Overview
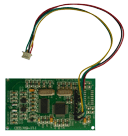
RFID systems consist of three core components: tags, readers, and middleware.
- RFID Tags: These small devices contain a microchip and antenna. They can be either passive (powered by the reader’s signal) or active (equipped with their own power source).
- RFID Readers: These devices send and receive radio signals, allowing them to detect and authenticate RFID tags within range.
- Middleware: This software connects the RFID system to an attendance or access control database, ensuring that data is processed and stored accurately.
When an RFID tag comes within the reader’s range, the tag’s information is captured and transmitted to the middleware, enabling seamless and real-time tracking for attendance systems or restricted area access.
The Role of RFID in Modern Attendance Systems
RFID technology has become a cornerstone in modern attendance systems. Unlike traditional methods such as manual logbooks or barcode scanners, RFID provides a contactless, automated solution. This minimizes human error, enhances data accuracy, and saves time. Organizations benefit from streamlined employee tracking, automated reporting, and integration with payroll systems, making RFID a valuable tool for both small businesses and large enterprises.
Improving Accuracy in Access Control Through RFID
RFID technology significantly reduces inaccuracies common in traditional access control systems. With RFID, there is minimal risk of duplication, forgery, or unauthorized access. Real-time authentication ensures only authorized personnel gain entry, making workplaces more secure and compliant with regulations. For attendance systems, RFID eliminates discrepancies in time logs, offering precise data for workforce management.
Advantages of RFID-Based Attendance Systems
Speed and Efficiency
RFID systems process data almost instantaneously, enabling quick identification without delays. This is especially useful for managing high-traffic areas like office buildings, factories, or educational institutions.
Contactless Operation
The contactless nature of RFID ensures hygiene and reduces wear and tear on devices, making it ideal for environments with high interaction rates. Employees can simply walk past an RFID reader without needing physical interaction.
Scalability for Large Enterprises
RFID systems are highly scalable, accommodating thousands of users. Whether it’s a small office or a multi-location enterprise, RFID solutions can be tailored to meet specific needs, ensuring seamless integration across all levels.
Challenges in Implementing RFID for Access Control
Security Concerns and Data Breaches
While RFID offers robust access control, it is not immune to security threats. Unauthorized readers or malicious actors could potentially intercept signals. Implementing encryption and authentication protocols is essential to safeguard sensitive data.
Cost Implications
The initial cost of RFID hardware and installation can be higher compared to traditional systems. However, the long-term savings in efficiency and reduced errors often outweigh the upfront investment.
Compatibility with Existing Systems
Integrating RFID technology into legacy systems can be challenging. Organizations must ensure that their current infrastructure supports RFID or invest in upgrades, which may require additional resources and planning.
Comparison of RFID with Traditional Access Control Technologies
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has brought a significant transformation to access control systems, offering advanced features compared to traditional technologies. Unlike conventional methods such as barcodes, magnetic stripe cards, and biometric systems, RFID provides a seamless, non-contact, and efficient experience. RFID tags can store vast amounts of data and communicate over greater distances without the need for physical alignment, making them a superior choice for large-scale applications in attendance systems and access control.
Barcode vs. RFID
Barcodes are one of the earliest technologies used in access control. They are inexpensive and easy to implement but come with significant limitations:
- Manual Alignment: Barcodes require precise alignment for scanning, which can slow down access processes.
- Limited Security: Barcodes are easy to replicate, making them less secure for access control.
- Data Capacity: They can only store limited information.
In contrast, RFID tags do not need direct line-of-sight alignment and offer enhanced security through encrypted communication. Additionally, RFID can handle dynamic attendance system data updates, making it ideal for workplaces requiring high accuracy and efficiency.
Magnetic Stripe Cards vs. RFID
Magnetic stripe cards have long been used for access control due to their simplicity. However, they face challenges such as:
- Wear and Tear: Physical swiping leads to deterioration over time.
- Security Risks: Magnetic stripes are vulnerable to duplication and tampering.
- Manual Interaction: Users need to swipe cards, which can delay access.
RFID addresses these challenges by offering a contactless, durable, and secure solution. With RFID, employees and visitors can seamlessly interact with attendance systems and access points without delays.
Biometric Systems vs. RFID
Biometric systems, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, are widely used for their high level of security. However, they have certain drawbacks:
- Environmental Sensitivity: Biometric systems may struggle in dusty, wet, or extreme environments.
- Cost: They often involve higher installation and maintenance costs.
- User Privacy Concerns: Employees may feel uneasy about sharing biometric data.
- RFID systems provide a middle ground, offering robust security without privacy concerns. Additionally, RFID tags can be easily integrated with biometric systems for dual authentication in advanced access control systems.
Applications of RFID in Industrial and Governmental Sectors
RFID technology has found extensive applications in both industrial and governmental sectors:
Industrial Sector:
- Tracking employee attendance and movement across large facilities.
- Managing inventory and supply chain processes efficiently.
- Restricting access to sensitive zones, such as laboratories or manufacturing units.
Governmental Sector:
- Monitoring attendance systems in public institutions.
- Managing access to secure areas in government buildings.
- Enhancing citizen services, such as smart ID cards and public transportation systems.
RFID's ability to improve security, efficiency, and accuracy makes it an indispensable tool in these sectors.
The Role of RFID in Enhancing Workplace Security
Workplace security is a critical concern for businesses, and RFID technology plays a pivotal role in addressing it. RFID-enabled access control systems ensure that only authorized individuals can enter specific areas, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. In addition, RFID tags can be programmed to provide time-stamped data, helping organizations monitor employee attendance and track access activities in real time. This data not only improves security but also aids in workforce management.
Future Trends: Integrating RFID with IoT and AI for Smarter Access Control
The future of RFID lies in its integration with emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- IoT Integration: RFID tags can communicate with connected devices to create intelligent access systems, such as automated door locks and real-time occupancy monitoring.
- AI Enhancement: Machine learning algorithms can analyze RFID data to identify patterns, predict security threats, and optimize access control systems.
These advancements will make RFID-based attendance systems more adaptive and efficient, further solidifying their role in modern workplaces.
Case Studies: Success Stories of RFID in Attendance and Access Control Systems
- Automotive Industry: A global automobile manufacturer implemented RFID-based attendance systems to monitor employee shifts and control access to high-security areas. The system reduced unauthorized access by 40% and improved attendance accuracy.
- Healthcare Sector: A hospital adopted RFID to manage staff attendance and secure access to sensitive areas, such as operation theaters and pharmacies. The technology enhanced operational efficiency and patient safety.
- Educational Institutions: Universities have successfully used RFID for student attendance systems and access control in libraries, ensuring a safe and efficient campus environment.
Conclusion: Is RFID the Future of Access Control?
With its superior features and adaptability, RFID technology is shaping the future of access control systems. Its ability to provide contactless, secure, and scalable solutions makes it a preferred choice for industries and organizations worldwide. As RFID continues to evolve, particularly through integrations with IoT and AI, its applications in attendance systems and access control will become even more transformative, paving the way for smarter and more secure workplaces.