Known as HMI, a human-machine interface, gesture recognition technology is a user interface that presents data to users about the state of a process or system. It can accept and implement the operator's control instructions. Typically such information is displayed in a graphic format called a GUI, which stands for the graphical user interface. As the name implies, gesture recognition is a type of computing user interface that allows computers to capture and recognize human movements or gestures and convert that information into a data stream, which can then be used for various digital purposes.
Instead of typing with keys or tapping on a touchscreen, a gesture recognition system perceives and understands movements as a primary input data source.
Gesture recognition systems can be either a touchless system or a touch-based system. Therefore, by employing gesture recognition controls, the need for interacting with physical devices, especially the mouse, keyboards, and buttons, will be diminished for users. Combining other advanced user interface technologies, specifically voice commands and face recognition gesture recognition, can create a richer user experience.
What is a gesture?
As per Oxford Dictionary, a gesture is defined as “a movement of part of the body, especially a hand or the head, to express an idea or meaning. Kurtenbach and Hulteen described it as A gesture is a motion of the body that contains information. Gestures are communicative, meaningful body motions, i.e., physical movements of the fingers, hands, arms, head, face, or body to convey information and interact with the environment.
Spontaneous gestures make up some 90% of human gestures. People make use of gestures even while talking on the telephone; blind people commonly gestures while talking. Across cultures, the speech-associated motion is natural and common.
Three functional roles of human gesture:
- To communicate meaningful information.
- To manipulate the environment.
- To discover the environment through tactile experience.
What is gesture recognition technology?
Gesture recognition is classified as a type of touchless user interface (TUI). Unlike a touchscreen device, TUI devices are controlled without touch. A voice-controlled smart speaker like Google Home and Amazon Alexa are prime examples of TUIs. However, gesture recognition is also a type of TUI, as it’s also controlled without touch. With that said, many devices that support gesture recognition also support touchscreen.
While there are many different types of gesture recognition technology, they all work on the same basic principle of recognizing human movement as input. The device features one or more sensors or cameras that monitor the user’s activity. When it detects a signal that corresponds with a command, it responds with the appropriate output. This may be unlocking the device, launching an app, changing the volume, etc.
Working of Gesture Recognition Technology:
Gesture recognition technology is becoming more and more popular. Gesture recognition is the mathematical interpretation of a human motion by a computing device. Gestures are most often used for input commands. Recognizing gestures as input allows computers to be more accessible for the physically impaired and makes interaction more natural in a gaming or 3D virtual reality environment.
Gesture technology follows a few necessary states to make the machine perform in the most optimized manner. These are:
- Wait: In this state, the machine is waiting for the user to perform a gesture and provide input.
- Collect: After the gesture is being performed, the machine gathers the information conveyed by it.
- Manipulate: In this state, the system has gathered enough data from the user or has been given input. This state is like a processing state.
- Execute: In this state, the system performs the task that has been asked by the user to do so through the gesture.
Devices that work on this technology usually follow these stages. Still, their duration might vary from machine to machine depending on its configuration and the task it is supposed to do. The basic working of the gesture recognition system can be understood from the following figure:
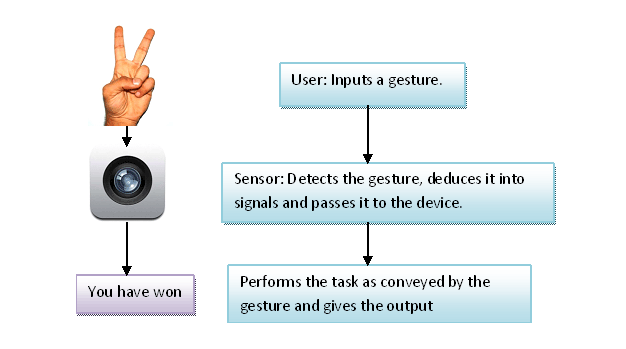
Hand and body gestures can be amplified by a controller that contains accelerometers and gyroscopes to sense tilting, rotation, and acceleration of movement, or the computing device can be outfitted with a camera so that software in the device can recognize and interpret specific gestures. A wave of the hand, for instance, might terminate the program.
Classification of Gestures:
Gestures can be categorized to fit into the following application domain classifications:
Pre-emptive Gestures:
A pre-emptive natural hand gesture occurs when the hand moves towards a specific control (device/ appliance). The hand approach's detection is used to pre-empt the operator's intent to operate a particular control.
Examples of such gestures could include the interior light's operation; as the hand is detected approaching the light switch, the light could switch on. If the hand is detected coming to the light switch again, it will switch off. Thus the hand movement to and from the device being controlled could be used as a pre-emptive gesture.
Function Associated Gestures:
Function Associated gestures are those gestures that use the natural action of the arm/hand/other body parts to associate or provide a cognitive link to the function being controlled. For example, moving the arm in a circle pivoted about the fan's elbow could signify that the operators wish to switch on the fan. Such gestures have an action that can be associated with a particular function.
An emotion of sadness can be conveyed through facial expression, a lowered head position, drooping shoulders, and lethargic movement. Similarly, a gesture to indicate “Stop!” can be communicated with the help of a raised hand with the palm facing forward or an exaggerated waving of both hands above the head.
Context-Sensitive Gestures:
Context-sensitive gestures are natural hand gestures that are used to respond to operator prompts or automatic events. Possible context-sensitive gestures to indicate yes/no or accept/reject could be a thumbs-up and a thumbs-down. These could be used to answer or leave an incoming phone call, an incoming voice message, or an incoming SMS text message.
Natural Dialogue Gestures:
Natural dialogue hand gestures utilize natural gestures used in human to human communication to initiate a gesture dialogue with the vehicle. Typically this would involve two gestures being used, although only one gesture at any given time. For example, if a person fanned his hand in front of his face, the gesture system could detect this and interpret that he is too hot and would like to cool down.
Types of gesture recognition technology
There are multiple gesture recognition technologies, including miniature radar systems, cameras, and electrical near field sensing.
- Soli is one of the projects of Google's advanced technology and projects group or a tap. Soli is a radar-based gesture recognition technology that uses small high-speed sensors and data analysis techniques for detecting subtle motions with submillimeter accuracy. As an example, Soli allows users to issue commands to a computer by rubbing a thumb and forefinger together in predefined patterns.
- Camera-based or vision-based gesture recognition technology uses a camera or cameras to capture and drive human movements. Both 2D and 3D cameras can be employed together with computer vision for translating human gestures.
- Electrical near fields are generated by electrical charges and propagate three-dimensionally around the surface carrying the electrical charge. When an alternating voltage is applied, the resultant field is also alternating. When the alternating wavelength is much larger than an electron geometry, the result is a quasi-static electrical near-field that can be used for sensing conductive objects such as a human body. For example, when the operator's hand intrudes the filled, the fill becomes distorted. Specifically, the filled lines interrupted by the hand are shunted to the ground through the human body's conductivity.
Types of gesture recognition technologies in use currently are:
Vision-based Technologies
There are two approaches to vision-based gesture recognition:
Model-based techniques:
Some systems track gesture movements through a set of critical positions. When a gesture moves through the same critical places as a stored gesture, the system recognizes it. Other systems track the body part being moved, compute the motion's nature, and determine the gesture. The systems generally do this by applying statistical modeling to a set of movements.
Image-based methods:
Image-based techniques detect a gesture by capturing pictures of a user’s motions during the course of a gesture. The system sends these images to computer-vision software, which tracks them and identifies the gesture.
Electrical Field Sensing
The proximity of a human body or body part can be measured by sensing electric fields. These measurements can be used to measure the distance of a human hand or other body parts from an object; this facilitates a vast range of applications for a wide range of industries.
Applications of Gesture Recognition Technology:
While the initial need for gesture recognition technology improved human-computer interaction, it found plenty of applications as computers' usage went widespread. Currently, the following applications of gesture recognition technology are there:
In Video Game Controllers:
With the arrival of 6th generation video game consoles such as Microsoft X-Box with Kinect sensor, Sony PS3 with motion sensor controller, gesture recognition was widely implemented. In Sony PS3, users have to move the controller in such a way so that it imitates the action the user wants the character in the game to perform. In X-Box, the user is often the controller and has to complete all the physical movements they desire to do in the game. The Kinect sensor has a camera that catches the motions and processes them so that the character exactly does it.

Aid to physically challenge:
People who are visually impaired or have some other complexity in their motor functions can use gesture-based input devices so that there is no discomfort while they access computers.
Other Applications:
- Gesture recognition technology is gaining popularity in almost every area that utilizes smart machines. This technology can detail every part of location information about the airplanes near the airport in aircraft traffic controls. This can be used in cranes instead of remotes so that easy picking and shedding of load can be load at difficult locations.
- Smart TVs are now coming with this technology, making the user carefree about the remote and allowing them to use their hands to change the channel or volume levels. Qualcomm has recently launched smart cameras and tablet computers that are based on this technology. The camera will recognize the object's proximity before taking the picture and adjust itself according to the requirements.
- The tablet computers with this technology will ease the user's task to give presentations or change songs on his jukebox. Gesture recognition technology can also make the robots understand human gestures and make them work accordingly.
What benefits does gesture recognition technology offer?
Gesture recognition also opens the doors to a whole new world of input possibilities. Instead of being limited to traditional input forms, users can experiment with other gesture-based input forms. In addition to smartphones and tablets, gesture recognition is also found in automotive infotainment centers, video game consoles, human-machine interfaces, and more. You move your hand or finger in front of the sensor, and it responds accordingly. Because of its touchless approach, the device sustains less wear.

Gesture recognition challenges:
Latency:
One of the critical challenges in gesture recognition is that the image processing can be significantly slower, creating unacceptable latency for video games and similar applications. In addition to the technical challenges of implementing gesture recognition, there are also social challenges. Gestures must be simple, intuitive, and universally acceptable.
Robustness:
Some gesture recognition systems do not read motions accurately or optimally due to insufficient background light, high background noise, etc.
During the next few years, Gesture recognition is most likely to be used primarily in niche applications because making mainstream applications work with the gesture recognition technology will take considerable effort than it’s worth.