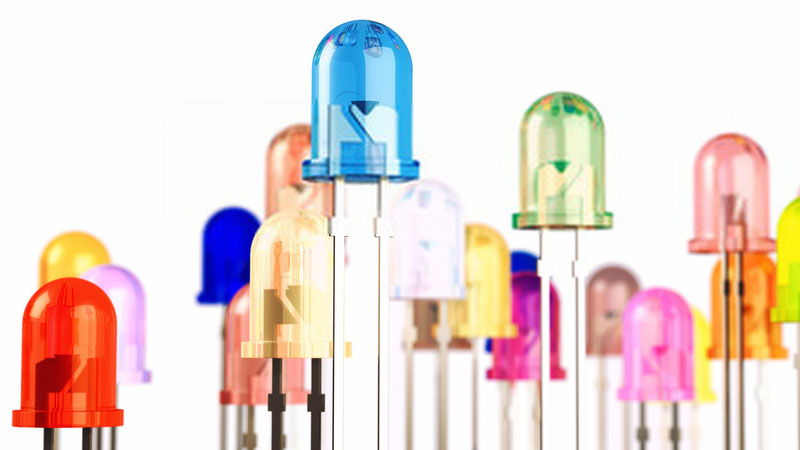
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a two-lead semiconductor light source. LED light is the result of the processing of two semiconductor elements called P and N. When these two elements are in direct contact, A P-N Junction connection is activated, and the LED imitates the light itself. P-N Junction connects a positive semiconductor to a negative semiconductor.
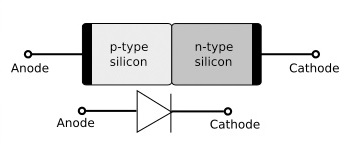
When a suitable voltage sends for guiding, The electrons can recombine with electron cavities inside the device and release energy.
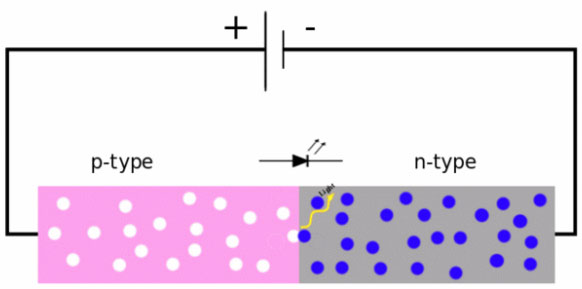
How does light emitting diode work?
LED bulbs embedded in electrical devices were red in the early days. LED bulbs have deficient energy consumption and long life than incandescent lamps. The first industrial production LEDs were introduced in 1962, and they were only in red color. The first light-emitting LED light was of low intensity and limited to red. Today, modern LEDs are available at visible wavelengths such as ultraviolet and infrared at high brightness.
Primary LEDs were often used as indicator lights for electronic devices as substitutes for small filament lamps. Over time, they were used to read numbers on screens and then on digital watches. Recent developments have LEDs suitable for environmental and work lighting. New LED lights have led to new displays and sensors with high switching rates in communication technology transfer.
- LEDs have many advantages over radiant light sources, including lower power consumption, longer life spans, improved physical strength, smaller size, and faster switching. Optical diodes are used in various applications such as air lighting, car headlights, advertising, general lighting, traffic signals, blinking camera, and clear wallpaper. Home lighting LEDs are much cheaper than fluorescent bulbs, they are also significantly more energy-efficient, and certainly, there are fewer environmental problems associated with their disposal.

LEDs types:
- LEDs are produced in different shapes. The plastic lens color is often the same as the actual color of the light, but not always. For example, purple plastic is often used for infrared lights. High-power modern lights such as lighting lights and the backlight are generally found in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) technology packages.
- SMT refers to the technology and how to install electronic components on a printed circuit board's surface.
LED colors:
Conventional LEDs are made from a variety of mineral semiconductor materials. Some LEDs emit infrared energy; such a device is known as an infrared diode or IRED (Diode Emitting Infrared).
- The RGB LEDs include red, green, and blue. Independently, each of the three RGB LEDs can produce a wide range of colors.
- White light can be produced by mixing different color lights. The most common way is to use red, green, and blue (RGB) since these electronic circuits need to control the composition and publish different colors. Because color LEDs usually have different publishing patterns. Even if they are made as unit units, these are rarely used to produce white light. However, this method is widely used due to the flexibility of mixing different colors, and in principle, this mechanism also has a high quantum efficiency in producing white light.
- There are many different types of color LEDs: Diode LEDs, 3D, and tetrachromatic LEDs. Several key factors that play a basic role among these different methods include color stability, color rendering feature, and brilliant effect.
Advantages of LED lights in comparison with incandescent lamps
- LED lights emit more light than incandescent bulbs.
- LEDs can pass light without color filters. This method is very efficient and can save a lot of costs.
- LED lights can quickly turn on in a fraction of a second.
- LED bulbs, unlike filament lamps, do not heat and have a longer life than they are.
- LEDs can be easily deployed for decades if properly installed.
Related posts: